What is in-place algorithm in data structures and algorithms
In-place algorithm
There are devices that don’t have enough
memory space. For example, mobile phones, PDA, etc. For these devices, the
problem is more time is spent on I/O (input/output) operation than calculation.
In-place algorithm - an algorithm that
uses a small constant amount of extra space in addition to the original input,
usually overwrite the input space.
Example:
Reverse the string “WELCOME”.
Method
1:
Assume that the letters are stored in an
array A1 as follows;
|
W
|
E
|
L
|
C
|
O
|
M
|
E
|
To reverse the string ‘WELCOME’, we can
create another array A2 and read A1 in reverse and paste each element in A2
from the beginning as follows;
 |
| Non-in-place algorithm uses O(n) extra space |
Drawback:
This method needs O(n) additional memory
space. That is, we create another array of same size and paste the characters
from the given string.
Method
2:
Assume that the letters are stored in an
array A1 as follows;
|
W
|
E
|
L
|
C
|
O
|
M
|
E
|
To reverse the string ‘WELCOME’, we can exchange
the element stored in the first index with the last, second index with the last
but one, and so on until entire string is reversed. You can observe it from the
figure below;
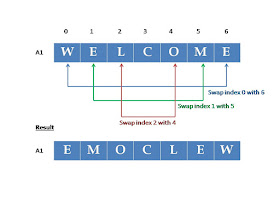 |
| In-place algorithm - uses O(1) extra space to swap |
Advantage:
This method implements in-place algorithm to reverse the given
string. O(1) constant extra space is used to reverse the string. [This
one character space is used to swap two characters from the string. Temp =
A1[0], A1[0] = A1[6], A1[6] = temp]
Example
in-place algorithms:
- Insertion sort
- Selection sort
Example
of not-in-place (out-of-place) algorithms:
- Merge sort
******************
in-place sorting algorithm
examples for in-place algorithm
how does in-place algorithm works
how does in-place algorithm save space
how much extra space an in-place algorithm need

No comments:
Post a Comment