Key differences between Internet Checksum and Cyclic Redundancy Check; differentiate between IC and CRC;
Internet Checksum (IC) Vs Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
IC and CRC are both error detection mechanisms to ensure data integrity after transmission across the network.
|
Internet Checksum (IC) |
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) |
|
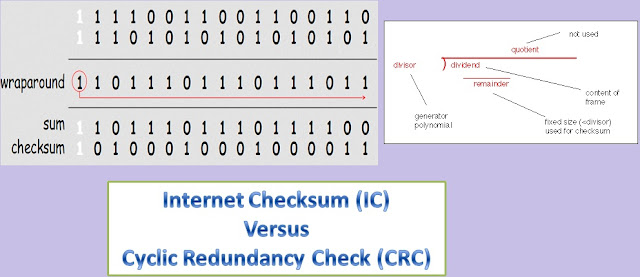
· Covers part of IP header (Network Layer), as well as TCP/UDP data (Transport Layer). · 16-bit modulo 2 arithmetic. Also known as “hash sum” · Done in software. · It can detect single-bit errors (please refer below) · Less complex. · Very weak error detection mechanism. · Oldest method used for data validation. |
· Used in many DLL (Data Link Layer) protocols, such as Ethernet and WiFi. · Typically 32-bit, sent as trailer. Also known as “polynomial code checksum” · Done in both software and hardware. · It can detect double-bit errors. (please refer below) · Increased complexity in the computation. · Very powerful error detection mechanism. |
Bit error – in a data sequence, change of bit 0 to 1 or vice versa.
Single-bit error – change of a single bit in the entire sequence that is transmitted
Double-bit error - change of two bits of data sequence
**************
Related links

No comments:
Post a Comment